Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) meaning has now become central to understanding one of the world’s most influential technologies. Today, AI is affecting a wide range of industries and shaping the future of human-computer interaction. From virtual assistants that understand human commands to complex algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data, artificial intelligence is redefining what machines can accomplish. This blog will cover the meaning of artificial intelligence, explore its history, highlight its benefits, and discuss its drawbacks, providing a thorough overview of this technology.
1. Artificial Intelligence Meaning
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally defined as a machine’s ability to mimic intelligent human behavior. This makes programming computers to execute things that normally require human intelligence, such as comprehending natural language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and making judgments. The term “artificial intelligence” refers to a wide range of technologies and procedures, including simple rule-based systems and complicated machine learning algorithms.
Key Concepts in AI:
Machine Learning: A subset of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without the need for precise programming. For example, a machine learning algorithm could use historical data to forecast future patterns.
f4ea0b
Deep Learning: A more advanced type of machine learning that use neural networks with multiple layers (thus the name “deep”) to examine numerous elements in data. Deep learning has led to essential advancements in image and speech recognition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): This enables machines to comprehend and interpret human language as it is spoken or typed. Chatbots, translation services, and virtual assistants such as Siri and Google Assistant are all examples of applications.
AI can be categorized into two primary types:
Narrow AI: This kind of artificial intelligence, also referred to as weak AI, is made to carry out a single task. Recommendation engines, facial recognition software, and even AI in video games that adjusts to player behavior are a few examples.
General AI: This type of AI, which is frequently referred to as strong AI or AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), would be able to comprehend, learn, and apply knowledge in a way that is identical to that of a human. Even if narrow AI has advanced significantly, researchers and theorists are still working toward general AI.
Importance of AI:
The importance of AI is in its capacity to handle and analyze huge volumes of data significantly more rapidly than humans. This capacity produces insights that influence operational effectiveness and decision-making in a number of sectors, such as healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment.
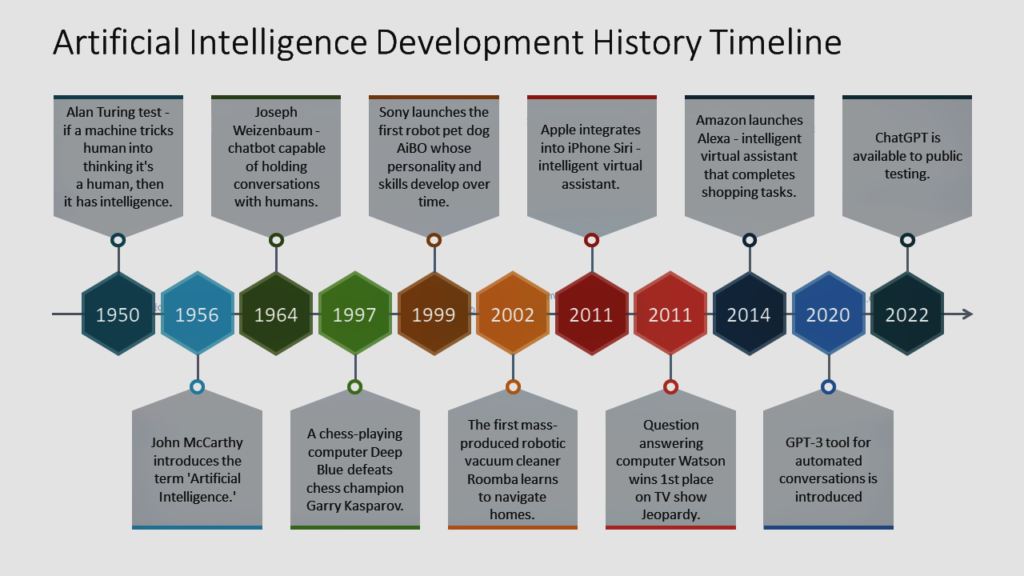
2. Artificial Intelligence History
The artificial intelligence history is rich and complex, marked by remarkable milestones and breakthroughs. Here is a timeline of key events that have shaped the development of AI:
- 1950s: The foundations of artificial intelligence were laid throughout this decade. Alan Turing’s key study, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” introduced the Turing Test, a point of reference for determining whether a machine has human-like intelligence or not.
- 1956: John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon organised the Dartmouth Conference, which is regarded as the birthplace of artificial intelligence as a field of study. It brought together significant figures in computer science and established the foundation for future study.
- 1960s: Early artificial intelligence algorithms, such as ELIZA, developed by Joseph Weizenbaum, displayed natural language processing skills. ELIZA could imitate a conversation by identifying keywords and reacting with predefined responses.
- 1970s: The creation of expert systems has now begun, with the goal of solving specific challenges in sectors such as health and engineering. One famous example is MYCIN, an expert system for diagnosing bacterial illnesses.
- 1980s: AI research suffered setbacks due to high expectations and little development, resulting in what is known as the “AI winter.” Funding fell as businesses and researchers battled to meet high goals.
- 1990s: Advances in machine learning and higher processing capacity fueled the rebirth of interest in artificial intelligence. In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated global chess champion Garry Kasparov, marking a key milestone in artificial intelligence.
- 2000s: AI technologies began to spread through daily life. Search engines began adopting AI algorithms to imprve results, and recommendation systems appeared on sites such as Amazon and Netflix.
- 2010s and Beyond: The rise of deep learning has changed the AI environment. Breakthroughs in image and speech recognition have resulted in applications in a variety of fields, including autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, and language translation.
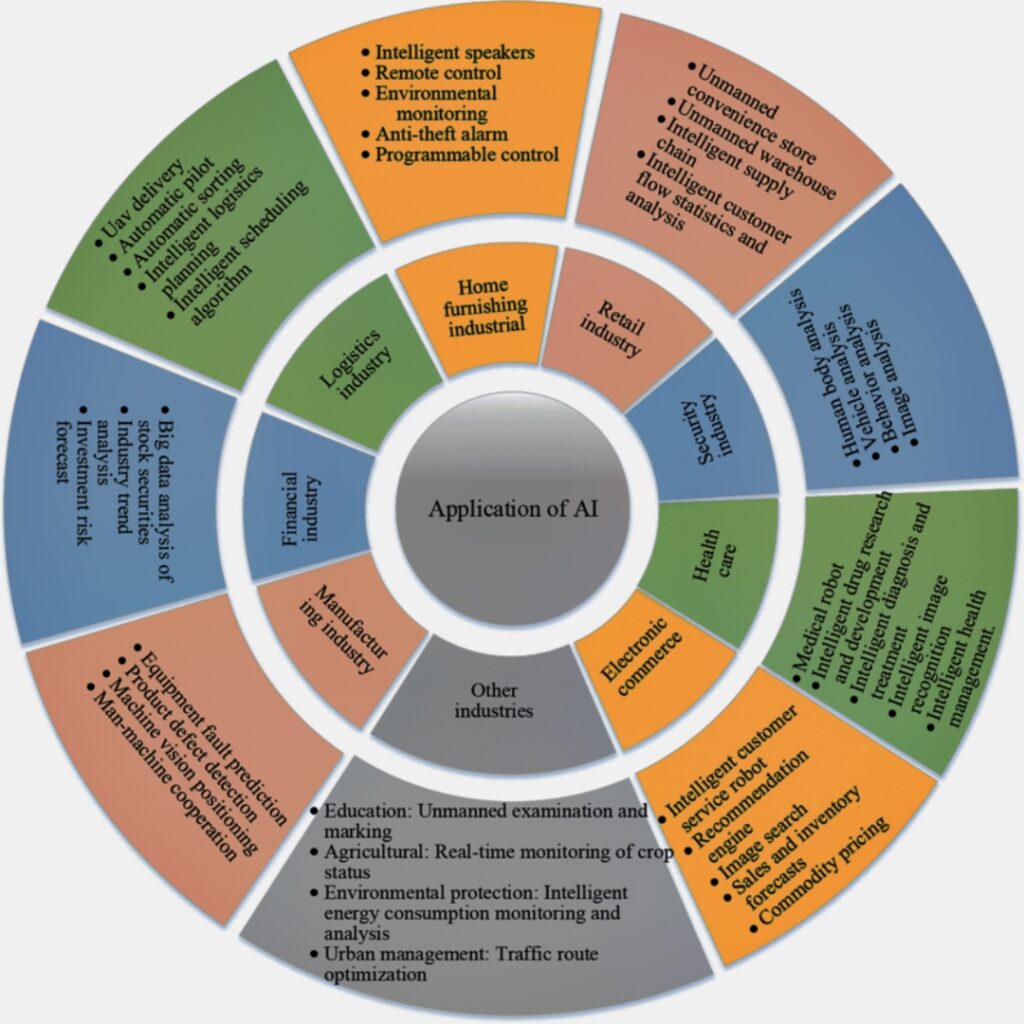
Current Landscape:
Today, AI is everywhere, with applications ranging from self-driving cars to smart home devices. It helps to increase productivity, automate jobs, and improve decision-making processes.
3. Artificial Intelligence Benefits
Artificial intelligence has several advantages that benefit a wide range of industries. Here are some important advantages:
3.1 AI in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence technology have transformed healthcare by boosting diagnoses and treatment choices. Machine learning algorithms can accurately detect irregularities in medical imaging such as X-rays and MRIs. For example, AI systems are being used to detect early indicators of diseases such as cancer, allowing for more timely intervention and better patient outcomes.
AI is also improving customised medicine by studying genetic data and customizing therapies for individuals. This level of customisation results in more effective therapies while lowering the chance of side effects .
3.2 AI in Finance
AI applications have a significant impact in finance. Algorithms examine market movements, evaluate credit risks, and detect fraudulent activity with surprising accuracy. AI-powered systems can monitor transactions in real time, reporting suspicious activity and stopping fraud before it occurs.
Furthermore, robo-advisors use AI to deliver customised investing recommendations based on individual risk profiles andfinancial objectives. This reduces barriers to financial planning, allowing more people to invest properly.
3.3 AI in Education
AI is transforming education by allowing for separate learning experiences. Intelligent teaching systems respond to individual learning styles and paces, giving personalised feedback and resources. This method allows students to absorb complicated concepts more efficiently.
Furthermore, artificial intelligence can automate administrative work, allowing educators to focus on teaching and student involvement. AI can also detect at-risk pupils through data analysis, allowing for immediate interventions to enhance their development.

3.4 AI in Everyday Life
AI has become an integral part of our daily routines. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant simplify tasks, from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices. These technologies enhance convenience and improve efficiency in managing daily activities. In entertainment, streaming platforms use AI algorithms to recommend movies and shows based on viewing history, creating a personalized experience for users. This not only increases user satisfaction but also boosts engagement and retention
Explore similar article
ChatGPT: Your digital AI friend and how to use it?

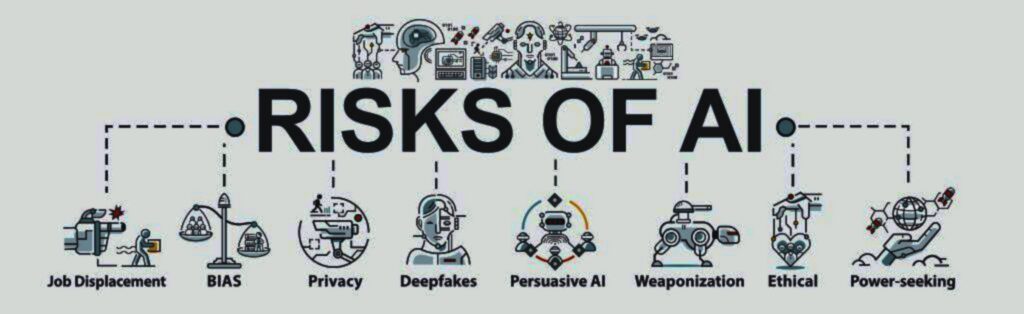
4. Artificial Intelligence Disadvantages
Despite its numerous advantages, artificial intelligence presents considerable problems and drawbacks. Here are some of the main concerns:
4.1 Privacy Concerns
AI systems frequently rely on large volumes of personal data to perform properly. This creates major privacy concerns, particularly about how data is collected, stored, and used. For example, facial recognition technology has raised concerns about surveillance and the erosion of private rights.
The risk of data breaches is equally significant. If sensitive personal information is compromised, the connection can be severe, including identity theft and other criminal acts. Ensuring strong data protection procedures is critical for reducing these dangers.
4.2 Job Displacement
AI-driven automation threatens to destroy many employment, particularly in businesses that rely on routine operations. For example, the manufacturing and retail industries have experienced major job losses as robots and AI systems take over tasks previously occupied by people.
While AI opens up new career prospects in technology and data analysis, the transition might be difficult for individuals in affected areas. Reskilling and upskilling activities are critical for assisting displaced workers in adapting to the changing labour market.
4.3 Ethical and Bias Issues
AI systems are not immune to biases in the data from which they are trained. If a machine learning model is trained using biassed data, it may produce biassed results. This is especially concerning in fields such as hiring procedures, law enforcement, and loan approvals, where biassed algorithms can inflame socioeconomic inequities.
Furthermore, the lack of directness in the AI decision-making process creates ethical concerns. When algorithms make important decisions that influence people’s lives, understanding how they are made is critical for accountability.
4.4 Dependence on Technology
As we rely more on AI systems to make decisions, there is growing concern about technological addictedness. Individuals’ critical thinking and problem-solving abilities may suffer as a result of this reliance. In addition, system failures or inaccuracies might have serious involvement.
5. Conclusion
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a game-changing technology with the potential to change many industries and improve our daily lives. Understanding its meaning and historical context allows usto comprehend its huge significance, which ranges from improved healthcare to automated financial operations.
While AI has various benefits, such as enhanced efficiency and personalized experiences, it also raises serious concerns about privacy, job displacement, and ethical difficulties. As we continue to use AI into our lives, we must address these challenges properly.
By balancing innovation and ethical considerations, we may realize AI’s full potential to assist society while limiting threats. Adopting AI wisely will allow us to establish a future in which technology works for the benefit of humanity.
Check out recent AI advancements here
If you have any query feel free to contact us